Introduction:
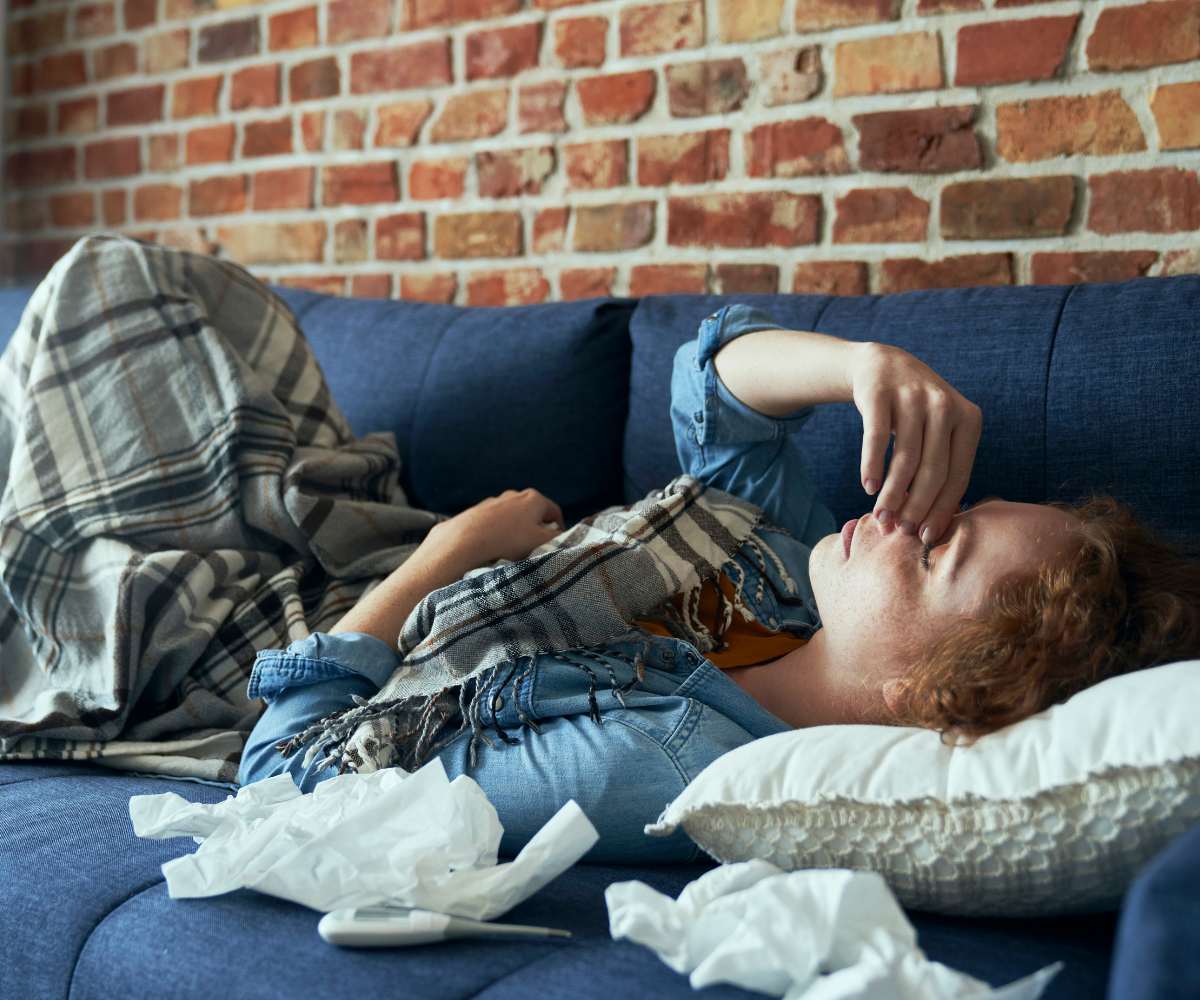
Sinus infections, or sinusitis, can be a source of discomfort and frustration. Many individuals turn to antibiotics for relief, but understanding the appropriate use of these medications is crucial. In this article, we’ll explore the role of antibiotics in treating sinus infections and provide valuable insights for effective management.
Types of Sinus Infections:
Acute Sinusitis: Typically caused by a bacterial infection, acute sinusitis may benefit from antibiotics if symptoms persist or worsen after a week.
Viral Sinusitis: Often associated with the common cold, viral sinusitis is not responsive to antibiotics. Understanding the root cause is vital for determining the appropriate treatment approach.
When Antibiotics Are Necessary:
Bacterial Infections: If a bacterial infection is suspected or confirmed through diagnostic tests, antibiotics may be prescribed to target the specific bacteria causing the sinusitis.
Persistent Symptoms: When symptoms persist beyond a week or worsen despite home remedies, antibiotics may be considered to prevent complications.
Antibiotic Treatment Guidelines:
Narrow-Spectrum Antibiotics: Choosing antibiotics that specifically target the identified bacteria helps minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance and side effects.
Complete Course: It’s crucial to complete the entire antibiotic course prescribed by the healthcare professional, even if symptoms improve before completion.
Home Remedies and Non-Antibiotic Approaches:
Nasal Irrigation: Saline nasal sprays or neti pots can help flush out mucus and alleviate congestion.
Steam Therapy: Inhaling steam can provide relief by reducing nasal congestion and promoting drainage.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps thin mucus, making it easier to expel.
Preventing Antibiotic Resistance:
Antibiotic Stewardship: Using antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary helps prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Follow Professional Advice: Always follow the advice of healthcare professionals regarding antibiotic use and complete the prescribed course.
Seeking Professional Guidance:
Consultation with Healthcare Providers: If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Tests: Diagnostic tools such as imaging or nasal swabs may be employed to identify the cause of sinusitis and guide treatment decisions.
Conclusion:
While antibiotics play a vital role in treating bacterial sinus infections, it’s essential to use them judiciously. Understanding the type of sinus infection and seeking professional guidance for an accurate diagnosis ensures that treatment is tailored to individual needs. Combining antibiotics with supportive measures and non-antibiotic approaches provides a comprehensive strategy for managing sinus infections and promoting overall sinus health.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only, and individuals should consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.